Strategic Foundations: Unveiling the Essence of Epidemic Resilience Planning Initiatives
Epidemics pose formidable challenges to societies worldwide, demanding strategic planning initiatives to build resilience against unforeseen health threats. This article delves into the multifaceted landscape of epidemic resilience planning, exploring the key initiatives that fortify communities and healthcare systems.
Understanding Epidemic Resilience Planning
Epidemic resilience planning is a proactive approach aimed at enhancing the capacity of communities and healthcare systems to withstand, respond to, and recover from the impact of infectious disease outbreaks. It involves strategic foresight, collaboration, and the implementation of targeted initiatives to ensure readiness for a spectrum of potential health crises.
Risk Assessment and Preparedness
At the core of epidemic resilience planning is a comprehensive risk assessment. This initiative involves evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of various infectious disease scenarios. By understanding the risks, communities and healthcare systems can tailor their preparedness strategies, ensuring that resources are allocated where they are most needed.
Strengthening Healthcare Infrastructure
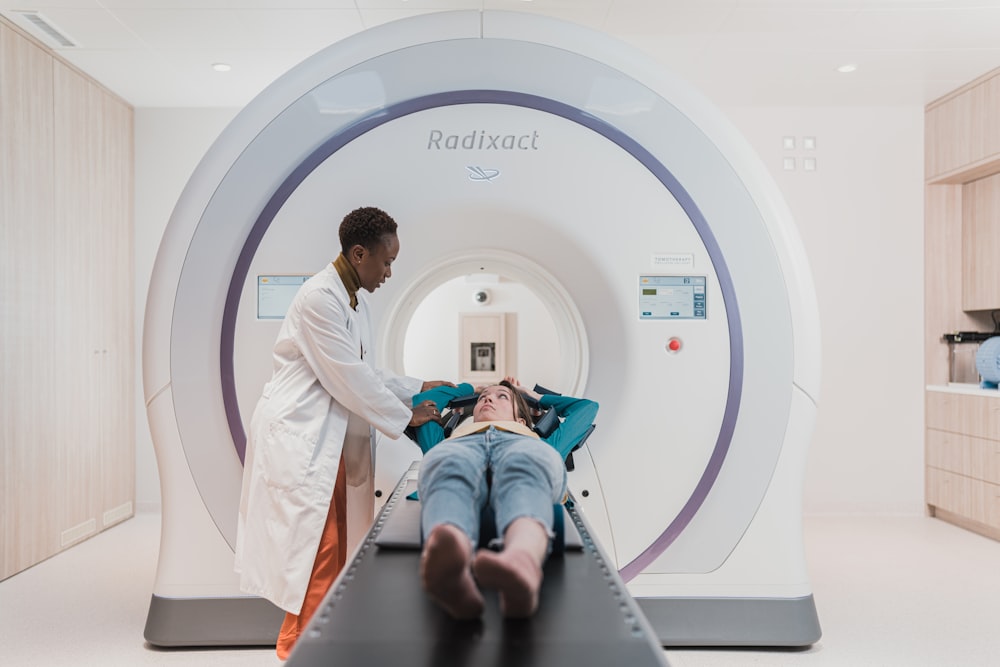
A resilient healthcare infrastructure is a linchpin in effective epidemic response. Initiatives focusing on infrastructure include expanding hospital capacities, ensuring a robust supply chain for medical resources, and investing in advanced medical technologies. These measures fortify healthcare systems, enabling them to handle surges in cases and provide optimal care during epidemics.
Community Engagement and Education
Empowering communities through engagement and education is a fundamental initiative in epidemic resilience planning. This involves disseminating accurate information about infectious diseases, preventive measures, and the importance of early reporting. Informed communities become active partners in the response effort, contributing to the overall resilience of the population.
Development of Early Warning Systems
Early warning systems play a pivotal role in epidemic resilience planning. These systems utilize data analytics, surveillance, and real-time monitoring to detect potential outbreaks at their nascent stages. By identifying patterns and trends, early warning systems enable timely interventions, minimizing the spread of infectious diseases and reducing the impact on public health.
Research and Innovation for Adaptive Responses
The dynamic nature of infectious diseases requires continuous research and innovation. Epidemic resilience planning initiatives include fostering research in virology, epidemiology, and public health. Innovations such as rapid diagnostic tools, antiviral medications, and vaccines contribute to adaptive responses, ensuring that healthcare systems stay ahead of emerging health threats.
Collaboration at National and International Levels
Collaboration is a cornerstone of effective epidemic resilience planning. Initiatives involve forging partnerships at national and international levels, facilitating the exchange of information, resources, and expertise. Collaborative efforts enhance the collective capacity to respond to epidemics, creating a network of support for communities around the globe.
Psychosocial Support and Mental Health Initiatives
Epidemics take a toll not only on physical health but also on mental well-being. Resilience planning initiatives recognize the importance of psychosocial support and mental health initiatives. These include providing counseling services, creating community support networks, and raising awareness about the psychological impact of epidemics.
Flexible Response Strategies
Adaptive and flexible response strategies are crucial components of epidemic resilience planning. Initiatives in this realm involve scenario planning, regular drills, and the development of response frameworks that can be adjusted based on the evolving nature of infectious diseases. Flexibility ensures that responses remain effective in the face of uncertainty.
Post-Epidemic Evaluation and Continuous Improvement
An often overlooked but vital initiative is the post-epidemic evaluation and continuous improvement process. After an epidemic, resilience planning involves assessing the effectiveness of the response, identifying strengths and weaknesses, and incorporating lessons learned into future planning initiatives. Continuous improvement ensures that resilience strategies evolve with the changing landscape of infectious diseases.
Conclusion: Nurturing a Resilient Future
In conclusion, epidemic resilience planning initiatives form the bedrock of preparedness against infectious diseases. By embracing proactive risk assessment, strengthening healthcare infrastructure, engaging communities, and fostering international collaboration, societies can nurture a resilient future. Epidemic resilience planning is not a static concept but a dynamic and evolving strategy to safeguard global health.
For more information on epidemic resilience planning initiatives, visit Healthcare Systems.